|
| Could BIBA be the active ingredient in a pill that solves your weight problems once and for all? Or is that too good be true? |
As Karima Begrich et al. point out in a more recent review of the literature, "experimental evidence [... also] suggested that BAIBA could reduce body adiposity through increased leptin expression and secretion" (Begriche. 2010).
Some people say that caffeine is the last real "fat burner" left on the market
Unfortunately, it does not take long to find the first evidence that blows a hole into the neat "BAIBA could solve the diabesity epidemic"-theory. It comes right from one of the previously cited studies.
In their 2008 study, Begriche et al. were able to confirm that the provision of 100mg/kg per day (for humans that would be ~8mg/kg per day) of Beta-aminoisobutyric acid triggers significant reductions in body fat gain in lean mice (Figure 1, left).
Overall, it does thus appear as if Begrich's own conclusion that BAIBA supplements "may be indeed an attractive pharmacological strategy in order to prevent (and/or treat) obesity" (Begrich. 2010) is only partly warranted:
- While BAIBA may be useful to ameliorate the body fat gain in lean individuals and would thus in fact be an "attractive pharmacological strategy in order to prevent [...] obesity" (ibid.) in an obesogenic environment,
- it appears to be more than just 'a little too early' to assume that BAIBA supplements could also be used to "treat" (ibid.) obesity in individuals who are already carrying >50% more body fat on their frame than the average lean person.
It is however more than the fact that many of you are probably (still) lean that keeps BAIBA in the game: If you look at the data in Figure 2, it becomes obvious that BAIBA may do more than to prevent the body fat gain in people who have always been lean: its effect on leptin, in particular, could be of even greater use for people who have lost a significant amount of body fat and are now struggling with the nasty yoyo effect.
As you can see in Figure 2, in vitro data shows that the direct exposure of fat cells (adipocytes) of mice, which are at a particularly high risk of becoming obese, will trigger a significant increase in leptin and adiponectin production. Why's that important? Well, of these...
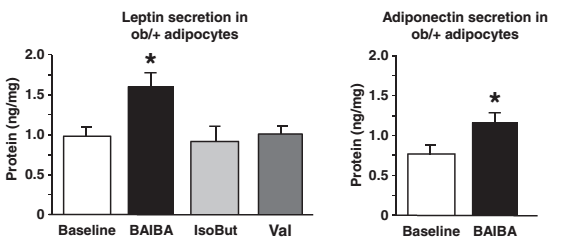 |
| Figure 2: The increase in adipocyte (=fat cell) leptin and adiponectin production that was observed in the petri dish is particularly interesting for people who have already lost a significant amount of body fat (Begrich. 2010). If it translates into in vivo human studies, it may help those people to stay lean and reverse "metabolic damage". |
the increase in adiponectin that is produced by one's fat cells has been linked to important health markers, like increased insulin sensitivity and improved markers of lipid management.![]()
Metabolic Damage, Energy Intake & the Human "Energy Thermostat" - An Update Based on Recent Studies | read it! - the increase in leptin production, however, may be of greater importance, because the diet- or rather fat-loss induced remodelling of the adipose tissue (many small empty fat cells) will reduce the production of the "you're fat enough" signal leptin and thus increase the risk of formerly obese individuals to regain every pound (or even more) of body fat they have painfully lost over months of hard dieting.
With that being said, the possibility that BAIBA may be able to reverse a potential cause of something that is often referred to as "metabolic damage" of which it appears as if it was at least partly triggered by a reduction in relative leptin production (i.e. the amount of leptin that is produced at a certain level of body fat) brings BAIBA back into the game.
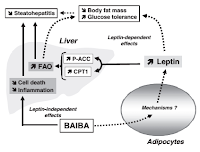
Bottom line: Whether an increase in leptin production is, as Figure 3 from Begrich's previously cited review suggests, the only (or at least the most important) mechanism of the beta-aminoisobutyric acid induced anti-obesity effect will yet have to be confirmed in future studies.
Comment on Facebook!
References:Comment on Facebook!
- Begriche, Karima, et al. "β‐Aminoisobutyric Acid Prevents Diet‐induced Obesity in Mice With Partial Leptin Deficiency." Obesity 16.9 (2008): 2053-2067.
- Begriche, Karima, Julie Massart, and Bernard Fromenty. "Effects of β‐aminoisobutyric acid on leptin production and lipid homeostasis: mechanisms and possible relevance for the prevention of obesity." Fundamental & clinical pharmacology 24.3 (2010): 269-282.
- Maisonneuve, Caroline, et al. "Mitochondrial and metabolic effects of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) in mice receiving one of five single-and three dual-NRTI treatments." Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 47.11 (2003): 3384-3392.
- Maisonneuve, Caroline, et al. "Effects of zidovudine, stavudine and beta-aminoisobutyric acid on lipid homeostasis in mice: possible role in human fat wasting." Antiviral therapy 9.5 (2004): 801-810.