I mean, if you could tell simply by looking at the standard labtests, most of which do include both triglycerides and HDL levels, you could save a lot of money on HOMA-IR or QUICKI tests and still be certain you suffer or don't suffer from insulin resistance and concomitantly increased cardiovascular disease risk.
Now the $64,000 question is: "Were Miguel Murguía-Romero et al. able to save your insurance company a lot of money, or not?"
The truth about cholesterol and heart disease...
... turned out to be more complex than the "pioneers" believed and complex "truths" have the nasty tendency to be self-contradictory and difficult to understand -- too difficult, in fact, to make it to the mainstream media and as it turned out obviously even too difficult for the average general practitioner, who is still easily convinced by the pharma reps that it was "best practice" to prescribe a statin and send the patient, who would be "unwilling and unable to change his dietary habits and increase his amount of physical activity, anyway" home with a script and patient information full of known side-effects most of the patients like to ignore.
 |
| Table 1: Talking about "metabolic syndrome" (MetS) what are the criteria to diagnose MetS? (Grundy. 2004) |
- a high level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL),
- a low level of high density lipoprotein (HDL),
- exuberant amounts of triglycerides (TRIGS),
With their recently conducted experiment, the scientists from the Stanford University Medical School did now try to elucidate whether the triglyceride / HDL ratio, which has been emerging in trials with old(er) individuals as one of the best markers of cardiovascular disease, would predict the CVD risk in 2244 healthy college students (17-24 years old) of Mexican Mestizo ancestry (1545 women and 699 men) and be able to identify younger individuals that are not merely at high risk of heart disease, but in whom this increased risk is direct consequence of being insulin resistant, as well.
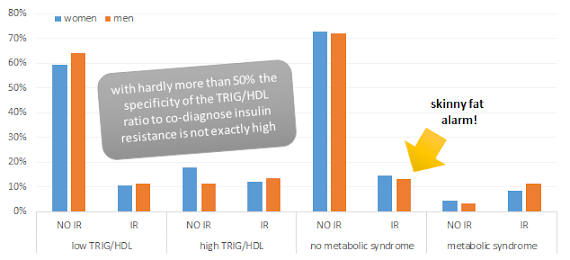
A closer statistical analysis did still reveal a slightly higher sensitivity for the TRIG/HDL ratio (53% / 55% in women / men) than for the criteria catalog that's used to "diagnose" metabolic syndrome (see table 1), which ended up at a meager sensitivity of 36% for women and 46% for men.
So where should your TRIG / HDL ratio be then?
In view of the results presented in the study at hand, the triglyceride-to-HDL ratio (TRIG / HDL) although it may not qualify as a diagnostic tool, is is a good indicator that there is something metabolically off. If that's your TRIG / HDL ratio that looks bad. Based on the figures in the study at hand this means:
- Your ratio of triglycerides to HDL-C should be < 3.5 if you are a man, or
- Your ratio of triglycerides to HDL-C should be < 2.5 if you are a woman
And don't forget that for most of the health-conscious victims of CVD, stress, not bad eating habits, or a lack of exercise, is the main problem - and that goes for both psychological andphysiological stress (including overtraining; learn more).
Bottom line:
| Suggested Read: "Eat Whole Eggs All Day and Throw Your Statins Away? 375x Increased Dietary Cholesterol Intake From Eggs Reduces Visceral Fat & Promotes Healthy Cholesterol Metabolism" - For most people eggs boost, not lower HDL and they are certainly not the reason for the ever increasing heart disease risk (learn more) |
In fact, the main message associated with the low sensitivity of the "MetSyn" criteria as a benchmark for insulin resistance, may well be that the mere absence of "above normal" levels for abdominal circumference, blood pressure and even blood glucose are not reliable criteria to determine, whether you are insulin resistant, or not. I'd say this is a message with public importance, especially for the skinny fats, who may well be the 15% and 13% of young men and women in the "no metabolic syndrome, but still insulin resistant"-group in the study at hand (see figure 1).
References:
- Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, Smith SC Jr, Lenfant C; American Heart Association; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation. 2004 Jan 27;109(3):433-8.
- Murguía-Romero M, Jiménez-Flores JR, Sigrist-Flores SC, Espinoza-Camacho MA, Jiménez-Morales M, Piña E, Méndez-Cruz AR, Villalobos-Molina R, Reaven RM. Plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, insulin resistance, and cardio-metabolic risk in young men and women. Journal of Lipid Research. 2013 [epub ahead of print]